Supporting Efficient Bulk Material Handling![]()
Bulk material handlers depend on the conveyor belt and idlers as foundational components of daily operations. The performance of the conveyor belt depends heavily on these often underappreciated supporting parts.
During a typical day, a conveyor belt transfers tons of bulk material, much of which can land on the belt with significant impact. Conveyor belts also operate in challenging environments with dust, dirt, humidity, and extreme temperatures.
These conditions can cause excessive wear and tear on the conveyor belt over time. When a conveyor belt deteriorates, it will often affect other areas throughout the load zone, complicate production, and increase safety hazards, downtime, and maintenance costs.
Common Conveyor Belt Problems
- Mistracking: When the belt slips to one side, it shifts the system out of alignment, causing uneven belt wear and reduced production efficiency.
- Slipping: Improper tension, often from worn head pulleys, can overstretch the belt and strain the system.
- Carryback: Residue from bulk materials accumulates on rollers and pulleys, creating safety hazards, equipment wear, and material loss.
- Spillage: Excess material can spill from the belt, leading to safety risks, production interruptions, and wasted product.
- Sagging: Unsupported weight can cause the belt to dip, creating gaps that allow material to escape.
Conveyor Belt Idlers
The conveyor belt alone cannot endure heavy-duty conditions without the proper support. Conveyor belt idlers play a critical role in maintaining system efficiency and preventing many common belt problems.
Idlers are rollers spaced beneath the carrying and return sides of the conveyor belt. They support the bulk material along the full belt length, preventing stretching, sagging, and premature failure. This ensures more consistent performance and longer belt life.
Most idlers are made of machined cast iron or heavy steel tubes mounted on antifriction bearings over a fixed steel spindle.
Primary Conveyor Belt Idler Components
- Housing: Seals and protects the idler’s inner components, ensuring concentricity and long life.
- Bearings: 2RS ball bearings handle radial and axial loads with minimal maintenance.
- Shafts: Cold-rolled steel secured to the frame, sized per CEMA class.
- Seals: Durable rubber shields bearings from dust, moisture, and contaminants.
- Snap rings: Lock seals and bearings in place to reduce wear.
Different idler types include carrying idlers, return idlers, impact idlers, and troughing idlers.
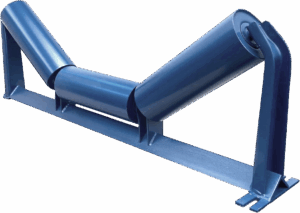
Benefits of Troughing Idlers![]()
Troughing idlers play a critical role in maintaining the efficiency and reliability of a conveyor belt system. They help shape the belt into a trough, allowing it to carry and contain bulk materials more effectively. By keeping material centered
and controlled, troughing idlers prevent spillage, minimize waste, and increase the belt’s overall load-carrying capacity.
Installed along the carrying side of the conveyor belt, troughing idlers guide the transition from impact zones where material is loaded into smoother conveying sections. They also assist in transitions between flat pulley areas, feeding points, or picking zones, helping to maintain consistent belt alignment and material flow.
Each troughing idler assembly typically includes a central roll with a fixed width and two or more wing rolls on either side. The depth of the trough can be adjusted by raising or lowering the wing rolls, allowing operators to fine-tune the belt’s trough angle to match the conveyed material type and volume.
For enhanced performance, troughing training idler frames are used in sections of the conveyor where alignment and tracking are critical. These self-adjusting idlers automatically correct belt misalignment within the troughing section, maintaining a consistent cross-sectional area for material transport. This not only supports stable belt operation but also reduces edge wear and the risk of material spillage.
By reinforcing belt stability, tracking, and carrying capacity, troughing idlers and troughing training idlers improve conveyor efficiency, extend belt life, and enhance overall safety in bulk material handling operations.
Load Rating: Choosing the Right Idler
Selecting the proper conveyor belt idlers depends on several key factors, including the bulk material being handled, conveyor belt speed, and operating conditions such as temperature, humidity, and loading impact. These variables directly influence the idler’s design, size, and load-carrying capacity.
Each idler must be correctly sized for the conveyor belt’s width and trough angle. The idler’s load rating, the specific load it can support at any point along the conveyor, determines whether it can handle the weight of the material and belt without premature wear or failure.
The CEMA (Conveyor Equipment Manufacturers Association) system classifies idlers by load-carrying capacity:
- CEMA B & C: Light to medium-duty applications such as grain or aggregate.
- CEMA D & E: Heavy-duty operations like mining, cement, and steel handling.
CEMA load ratings are generally based on a bearing L10 life of 30,000 or 60,000 hours with the idler roll rotating at 500 RPM. These standards help ensure that the idlers can withstand demanding conditions over extended service intervals.
When selecting the right idler, engineers must also consider the following dimensional and mechanical factors:
- Mounting length: Determines where and how the idler will be bolted to the conveyor structure.
- Roll diameter: Ensures sufficient strength and surface area for supporting material weight.
- Idler height: Prevents interference with other structures or components.
- Belt width and trough angle: Ensure proper fit and load distribution.
- Footstrap and slot dimensions: Guarantee secure mounting and alignment.
Correctly sized and rated Benetech conveyor belt idlers allow belts to perform at maximum efficiency even under extreme conditions. Properly engineered idlers also simplify maintenance by allowing quick, safe replacement—especially in high-impact loading zones.
Idler Spacing
Idler spacing significantly impacts belt support and profile. Too much distance can allow sagging, while too little can increase costs and power requirements.
Factors that will determine idler spacing include:
- Belt Weight
- Material Weight
- Idler Load Rating
- Belt Sag
- Idler Life
- Belt Rating
- Belt Tension
- Vertical-Curve Radius
Idlers should be spaced closely enough to fully support the belt under load. For example, carrying idlers for material with a bulk density of 100 lbs./ft³ may be spaced 48 inches apart, while return idlers may be spaced 120 inches.
For precise spacing guidance, a Benetech specialist can evaluate your application and recommend optimal idler placement for efficiency and durability.
Benetech Conveyor Belt Idlers
Precisely made and installed conveyor belt idlers are vital for efficient, long-lasting conveyor operation. As a global leader in bulk material handling, Benetech offers engineered idlers for industries ranging from underground mines to steel mills and cement plants.
Benetech Idlers:
- Exceed CEMA standard load ratings
- Available with standard or wide-base frames
- Fit any belt width or troughing angle
- Available in impact or steel rolls
Belt Support & Alignment Solutions:
- Steel & Impact Troughing Idlers
- Simple Slide Trougher
- Drop and Slide Trougher
- Replacement Rollers – Steel & Impact
- Standard Return Rollers
- Rubber Disk Return
- Simple Slide Returns
- Simple Slide Flat Carrying Idler
- Troughing Trainers
- Return Trainers
- Troughing MaxTracker
- Single Direction Return MaxTracker
- Warrior Impact Bed
- Warrior Roll & Guide Bed
- Support & Seal Bed
Benetech: Your Ally in Bulk Material Handling
Here at Benetech, we dedicate ourselves to the most important details of daily operations at a bulk material handling facility. We welcome each opportunity to answer your questions about greater productivity in the load zone. If you would ever like to discuss the right idlers for your conveyor belt, contact us at (630) 844-1300 to speak with a specialist.
Posted in Conveyor Belts, Transfer Systems, and Uncategorized